Characterization of materials and substances
Similar to conventional manufacturing processes, this is also true in the Laser material processing The materials used and their properties are crucial for the quality of the process. Excessive tolerances in the alloy composition can lead to unwanted rejects or defective products.
Materials characterization at the Bavarian Laser Center
Identification. Characterization. Optimization.
The Bavarian Laser Center has an extensive portfolio of Equipment and systems for the characterization of materials and components.
This way, we can help you optimize your laser processes. Because only those who fully understand what is being processed and what effects the processing has on a component can guarantee a reliable product.
Metallographic analysis
Our focus is on the analysis of cross-sections and longitudinal sections for the evaluation of welds. In our semi-automated metallography laboratory, equipped with various light microscopes, we achieve high throughput rates. This means that only a few hours elapse between conducting the experiment and evaluating the results.
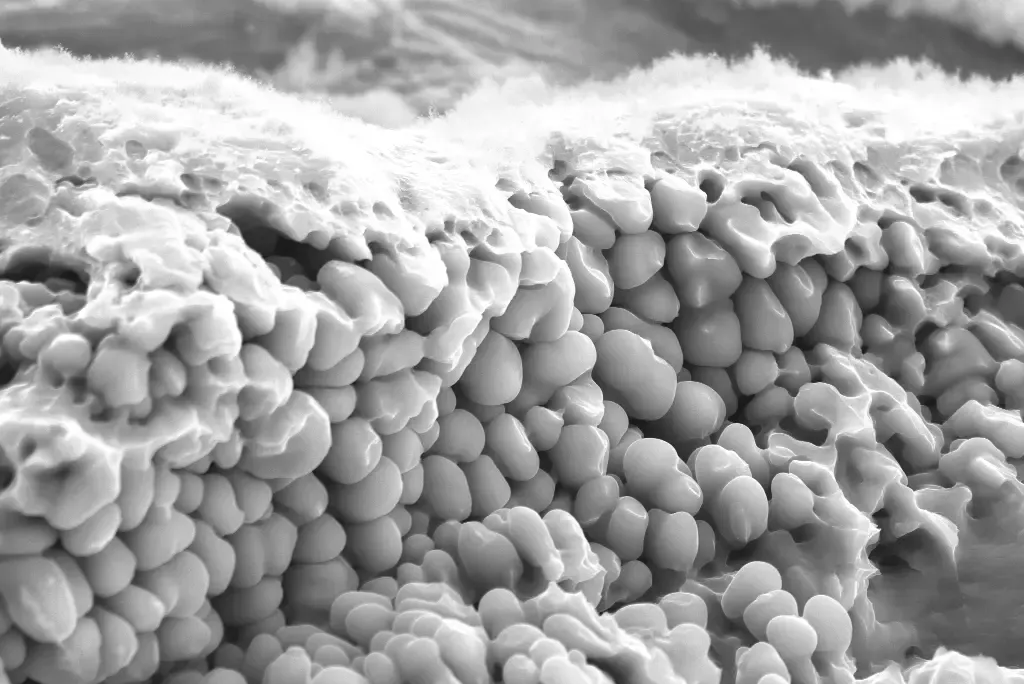
Scanning electron microscopy
Not all defects, effects, or properties can be detected using conventional light microscopy. By employing scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) equipped with EDX and EBSD, microstructural characteristics such as grain size, elemental distribution, and residual stress can be revealed. The result? A high-end evaluation of the process zone.
Hardness measurements
The hardness of a component or joint is the primary indicator of the material's strength. Whether you require macro- or microhardness measurements, we offer fast and straightforward support.
Tensile-compression test
Smoldering tensile-compression testing is the most common method for evaluating the quality of components. We test various joints and do not limit ourselves to standard tests.
Scherversearch
Shear tests can be used to characterize any joining situation with regard to its specific strength. This provides a reliable indication of the loads your component can withstand – or cannot.
Light Flash Analysis (LFA)
Light flash analysis can be used to measure temperature and thermal conductivity at temperatures up to 1,250 °C. This is ideal for evaluating thermal heat dissipation from the process as well as the expected heat load in the assembly.
Simultaneous thermal analysis (STA)
DSC and TGA measurements from room temperature to 1,600 degrees Celsius provide insights into heat flow and weight changes. They are therefore ideally suited for determining temperature-dependent phase transformations.
Spark spectrometry
Spark spectrometry allows for a fast and highly precise analysis of the chemical composition of your materials before and after the process.
Particle measurement
Especially in additive manufacturing, the shape and size distribution of the particles are crucial. Appropriate characterization of the starting material can prevent costly processes from occurring in the first place.
Characterization of your materials and components
You give us your samples, and we provide you with customized analyses.
Modern devices and measuring methods This enables us to identify crucial material properties, thereby optimizing your processes, accelerating your product development, and ensuring the quality of your components.
Please feel free to contact us and arrange a personal consultation. We look forward to hearing from you!
Advantages for industrial partners - Characterization of materials
The success of an application or product hinges on the right material. We have extensive experience in characterizing materials in our superbly equipped metallography laboratory. Benefit from our expertise. Expertise and speed.
01
extensive.
We characterize your material from A as in absorption to Z as in decomposition under thermal conditions.
02
fast.
Are you testing new materials and don't want to wait several weeks for feedback on their properties? With us, you get high-quality feedback in less than a week.
03
cost-effective.
External materials testing laboratories often charge high prices. We distinguish ourselves through low prices, as we have extensive experience in working efficiently with small batch sizes, gained from our daily research work.
04
All from one source.
You receive all information from a single source. This minimizes the risk of data or communication losses at now unnecessary interfaces.
Leave your callback request here.
Subscribe to Newsletter
FAQs on material characterization
Here you will find concise answers to questions about methods and applications of metallography.
What is metallography?
Materialography is the study of the microstructure of various material groups, such as metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Metallography is a subfield of materialography. Micrographs and microscopy are used to examine the structure and microstructure of materials. It serves for quality control, defect analysis, and materials development.
What methods are used in sample preparation?
- Sample separation
- Cold mounting or rapid mounting with UV-curing mounting medium
- Grinding and polishing (down to 50 nm)
- Etching of metals with various etching agents
- Light microscopy
- Scanning electron microscopy
- Hardness testing (Vickers)
What can be detected through metallography?
- Grain size and phase distribution
- Cracks, pores, segregations
- Weld quality and heat-affected zones or cut edge geometry
Which materials can be examined using metallographic methods?
- Metals and alloys (e.g., ferrous materials)
- Non-ferrous metals (e.g., copper, aluminum)
- Ceramics
- Plastics
- Coatings and thin films
Do you have any further questions about material characterization?
Don't hesitate to contact our team.